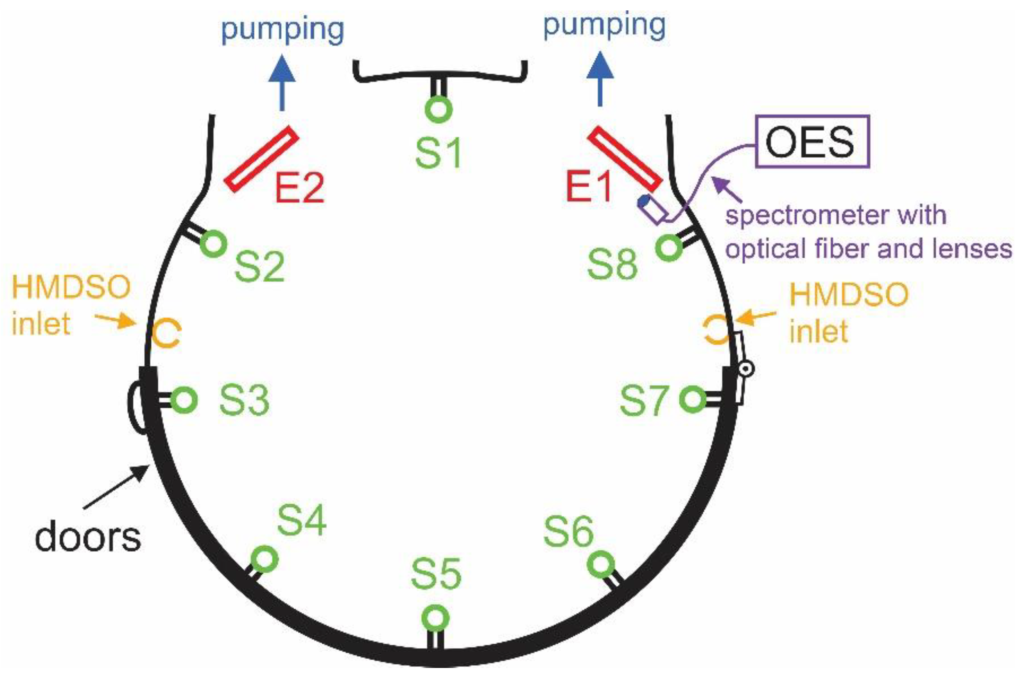
The deposition rates of protective coatings resembling polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) were measured with numerous sensors placed at different positions on the walls of a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) reactor with a volume of approximately 5 m3. The plasma was maintained by an asymmetric capacitively coupled radiofrequency (RF) discharge using a generator with a frequency 40 kHz and an adjustable power of up to 8 kW. Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) was leaked into the reactor at 130 sccm with continuous pumping using roots pumps with a nominal pumping speed of 8800 m3 h−1 backed by rotary pumps with a nominal pumping speed of 1260 m3 h−1. Deposition rates were measured versus the discharge power in an empty reactor and a reactor loaded with samples. The highest deposition rate of approximately 15 nm min–1 was observed in an empty reactor close to the powered electrodes and the lowest of approximately 1 nm min–1 was observed close to the precursor inlet. The deposition rate was about an order of magnitude lower if the reactor was fully loaded with the samples, and the ratio between deposition rates in an empty reactor and loaded reactor was the largest far from the powered electrodes. The results were explained by the loss of plasma radicals on the surfaces of the materials facing the plasma and by the peculiarities of the gas-phase reactions typical for asymmetric RF discharges.
Coatings 2021, 11(10), 1218; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101218
